Example Notebooks
The best way to learn how to use SciServer is to start from a working example – so we offer several examples from multiple science domains in a shared public Data Volume called Getting Started. Here are instructions for using these example notebooks to kickstart your research and teaching with SciServer.
Log in to SciServer, and you will see your Scierver Dashboard. Click on Compute to open a new window for SciServer Compute, where you will be able to create a virtual compute container for your work. Click on the Create Container button to set one up.
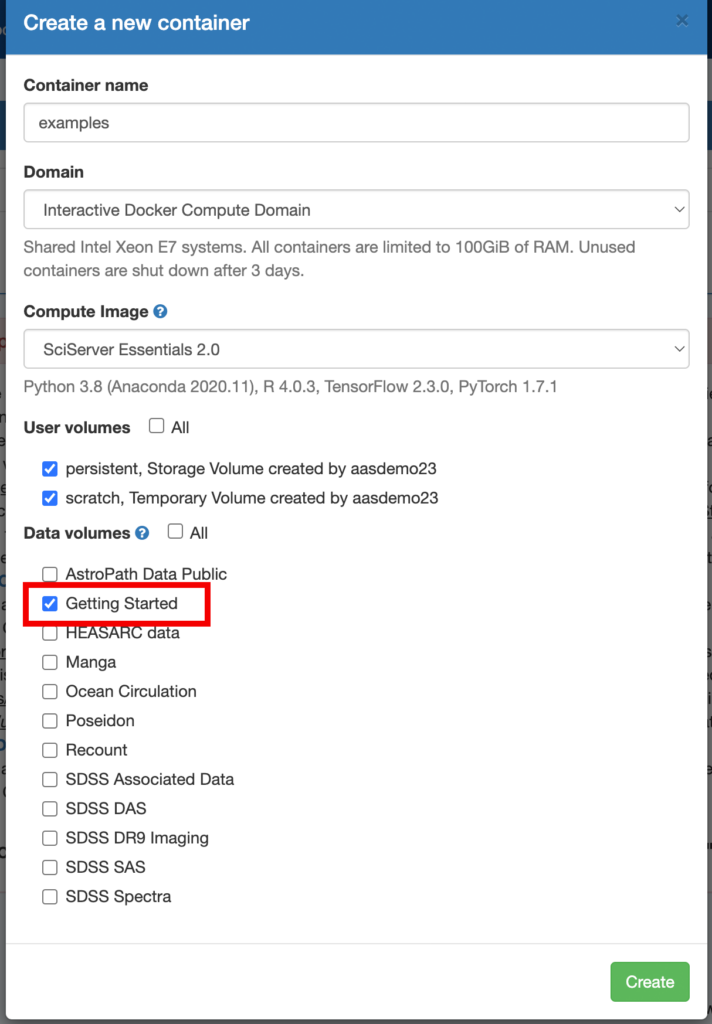
A new box will open over the page with options for your new container. Be sure to check the Getting Started checkbox so that you have access to the example datasets and notebooks. Click Create.
A new window will open showing you your files in the container you just created. Click on getting_started, then on Example-Notebooks to see the examples.
These example notebooks are shared among all users, so your first step is to copy them to a place where you can edit them and save your changes. You can do this either by copying the files to your Storage/persistent directory in the Dashboard, or by following the instructions in the starthere.ipynb Example Notebook.
NOTE: The Getting Started data volume also contains datasets that some of the example notebooks access. When you copy the example notebooks to your persistent space, be sure to copy only the Example-Notebooks folder, not the bigdata folder.